Technologies
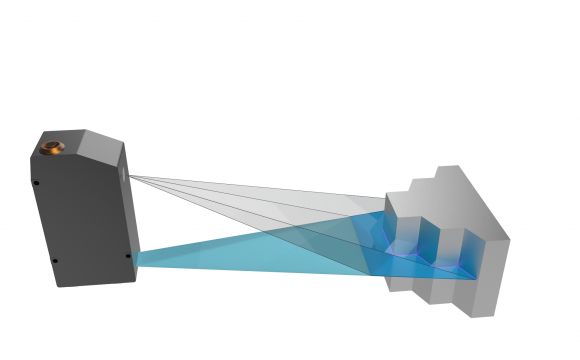
Triangulation
Measurement principle of a laser line triangulation sensor allows detection of a point or a line on different material surfaces.
A laser beam is projected on the object surface by laser diode or through prismatic optics broadening the laser beam into a trapezoidal plane. When intersecting with a surface the laser generates a point or a line that is then visualized and registered by a camera looking with an angle with the laser plane direction.
A controller calculates the distance of each point and the lateral position along the line (for a line sensor). The acquired values are integrated in a local sensor frame.
A 3D service scanning is possible in dynamic mode at several kHz frequencies with moving the sensor or the object.
The projected light is red or blue laser or structured light
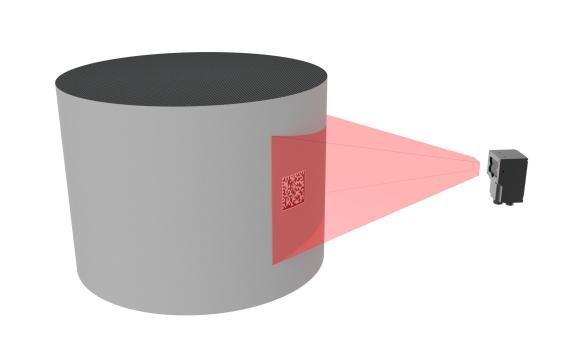
2D Vision
2D vision boils down to taking one or more images of the part to be controlled. The images can be obtained by one or more cameras.
The pictures are then digitized to be analyzed by a controller. The processed image can be used for dimensional analysis or to detect shapes.
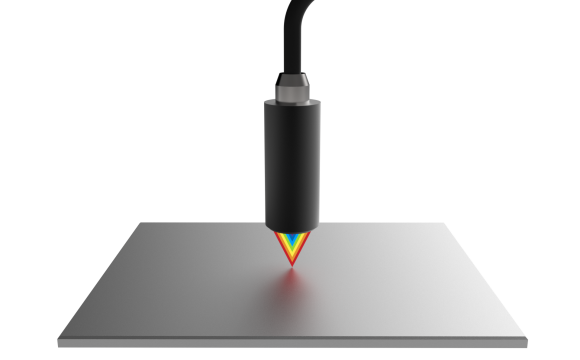
Interferometry & Confocal
An incident white light is diffracted and projected on the object surface providing a «color coding» along the optical axis. A spectrograph determines the unique wavelength that has been perfectly focused on the object and then reflected into the optical system. The object position is then accurately calculated using this back scattered radiation wavelength.
Confocal Chromatic technology gives access - on diffuses and reflecting surfaces - to very accurate (0.02 to 1 µm) displacement measurements with extremely high resolution with measurement ranges from 0.1 mm to few mm.
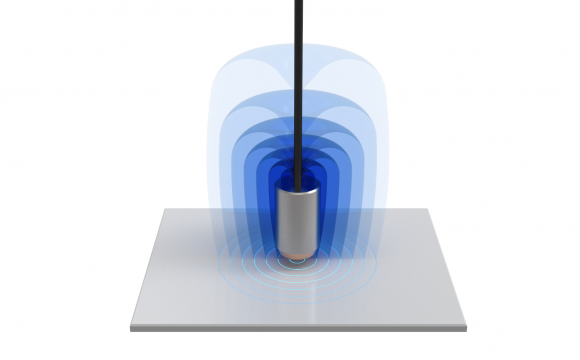
Electromagnetism
Eddy currents can be used to measure electrically conductive materials. (Ferromagnetic or not).
A high frequency alternating current flows through a coil. The electromagnetic field induces eddy currents in the measured object.
The impedance variation of the coil during the measurement is proportional to the distance separating it from the measured material.
